Posted by Admin on 21-09-2022 in Shiksha hub
PhD. in Biostatistics Theory and Methods OF inference, Admission Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
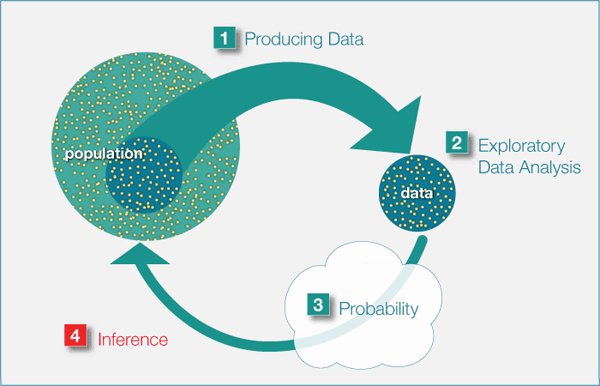
Introduction about PhD. in Biostatistics Theory and Methods OF inference
Introduction
Importance of Biostatistics in Research
The Growing Relevance of Ph.D. in Biostatistics
Understanding Biostatistics
Defining Biostatistics
Role in Healthcare and Medical Research
The Need for Advanced Study
Challenges in Data Analysis
Emerging Trends in Biostatistics
Ph.D. in Biostatistics: An Overview
Duration and Structure of the Program
Admission Requirements
Theoretical Foundation
Statistical Models and Methods
Probability and Inference
Practical Applications
Real-world Examples
Contributions to Public Health
Research Opportunities
Thesis and Dissertation Work
Collaborations and Publications
Skills Developed
Analytical Skills
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Career Prospects
Job Opportunities
Industry Demand for Biostatisticians
Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Statistical Challenges
Staying Updated with Advancements
Success Stories
Notable Individuals in Biostatistics
Impactful Research and Discoveries
Advice for Prospective Ph.D. Students
Preparation and Prerequisites
Navigating the Rigors of the Program
Future Trends in Biostatistics
Technology Integration
Evolving Research Areas
Introduction about Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference
Biostatistics, a pivotal field in the realm of research, plays a crucial role in deciphering complex data related to health and medicine. As we delve into the depths of scientific inquiry, the need for experts well-versed in statistical theory and methods becomes evident. This article explores the world of Ph.D. in Biostatistics, shedding light on its theoretical underpinnings and the practical applications that make it indispensable in modern research.
Understanding Biostatistics
Defining Biostatistics
Biostatistics, at its core, involves the application of statistical methods to biological and health-related data. It provides the tools necessary to analyze, interpret, and draw meaningful conclusions from complex datasets, aiding researchers in making informed decisions.
Role in Healthcare and Medical Research
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare and medical research, biostatisticians serve as navigators, guiding researchers through the intricacies of data analysis. Their expertise ensures that the results obtained are not only accurate but also hold significant implications for advancing medical knowledge.
The Need for Advanced Study
Challenges in Data Analysis
As the volume and complexity of biological data continue to burgeon, the challenges in analyzing and interpreting this information also escalate. Pursuing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics becomes imperative for those seeking to tackle these challenges head-on and contribute meaningfully to scientific advancements.
Emerging Trends in Biostatistics
The field of biostatistics is not static; it evolves in response to technological advancements and emerging research areas. A Ph.D. program provides the opportunity to stay at the forefront of these trends, ensuring that graduates are well-equipped to address the evolving needs of the scientific community.
Ph.D. in Biostatistics: An Overview
Duration and Structure of the Program
A Ph.D. in Biostatistics typically spans several years, during which students engage in rigorous coursework, research, and practical applications. The program's structure is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of both the theoretical and applied aspects of biostatistics.
Admission Requirements
Admission to a Ph.D. program in biostatistics is competitive, often requiring a strong background in statistics, mathematics, or a related field. Prospective students must showcase their passion for research and a clear vision for how their contributions will impact the field.
Theoretical Foundation
Statistical Models and Methods
Theoretical coursework delves into statistical models and methods, equipping students with the knowledge needed to design experiments, analyze data, and draw valid inferences. This foundational understanding forms the bedrock of their future research endeavors.
Probability and Inference
Probability theory and statistical inference are cornerstones of biostatistics. Ph.D. students delve into the mathematical intricacies of probability, learning how to make informed predictions and draw robust conclusions from data sets.
Practical Applications
Real-world Examples
The theoretical knowledge gained during the program finds practical applications in real-world scenarios. Ph.D. candidates engage in hands-on projects, applying statistical methods to solve tangible problems in healthcare and biological research.
Contributions to Public Health
Biostatisticians contribute significantly to public health by analyzing epidemiological data, conducting clinical trials, and informing health policies. The practical applications of a Ph.D. in Biostatistics extend beyond academia, directly impacting communities and populations.
Research Opportunities
Thesis and Dissertation Work
A cornerstone of Ph.D. programs is the research component. Students undertake extensive thesis and dissertation work, delving into specific areas of biostatistics and making original contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Publications
Ph.D. candidates often collaborate with leading researchers and contribute to publications that advance the understanding of biostatistics. These collaborations not only enrich their research experience but also contribute to the broader scientific community.
Skills Developed
Analytical Skills
The program hones analytical skills, allowing graduates to dissect complex data sets and derive meaningful insights. This skill set is invaluable in a data-driven world, where the ability to extract knowledge from vast datasets is a sought-after trait.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Ph.D. candidates develop critical thinking skills, enabling them to approach research questions with a discerning eye. The ability to solve complex problems is cultivated, fostering a mindset geared towards innovation and discovery.
Career Prospects
Job Opportunities
The demand for biostatisticians continues to rise, with opportunities spanning academia, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and government agencies. Ph.D. graduates find themselves well-positioned for roles that require expertise in data analysis and statistical interpretation.
Industry Demand for Biostatisticians
Industries increasingly recognize the value of biostatisticians in driving evidence-based decision-making. The pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors, in particular, are keen on recruiting Ph.D. graduates for their ability to navigate and interpret complex datasets.
Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Statistical Challenges
The field of biostatistics is not without its challenges. Ph.D. programs prepare students to overcome these challenges, whether they be related to data quality, study design, or the interpretation of statistical results.
Staying Updated with Advancements
In a rapidly evolving field, staying abreast of technological advancements is crucial. Ph.D. graduates are equipped with the skills and mindset to adapt to new methodologies and technologies, ensuring they remain at the forefront of biostatistical advancements.
How can I apply for admission to PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE Program?
Certainly! Applying for a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference program involves a series of steps. Here's a guide to help you navigate the application process:
Research Programs: Start by researching Ph.D. programs in Biostatistics that align with your academic and career goals. Look for universities or institutions renowned for their biostatistics departments and faculty expertise.
Review Admission Requirements: Thoroughly review the admission requirements for each program. Typically, these requirements include:
A Master's degree in a related field (sometimes a Bachelor's degree with exceptional qualifications may be accepted)
Strong academic transcripts demonstrating proficiency in statistics, mathematics, or a related discipline
Letters of recommendation from professors or professionals who can attest to your academic capabilities
A well-crafted statement of purpose outlining your research interests, career goals, and reasons for pursuing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics
Standardized test scores (e.g., GRE) may be required; check the specific requirements of each program
Prepare Application Materials: Collect all necessary documents, ensuring they meet the specific requirements of each program. This may include transcripts, letters of recommendation, a resume or curriculum vitae (CV), and a carefully written statement of purpose.
Standardized Tests: If required, register for and take any standardized tests (such as the GRE) well in advance. Be sure to send your scores to the chosen universities.
Contact Potential Advisors: Reach out to professors or researchers whose work aligns with your interests. Establishing contact can be beneficial and may enhance your application. Express your interest in their research and inquire about potential Ph.D. supervision.
Online Application: Complete the online application form for each program you wish to apply to. Ensure that all information is accurate and that you've uploaded all required documents.
Application Fee: Pay the application fee, if applicable. Some programs may require a fee to process your application.
Submit Application: Once all components are ready, submit your application before the deadline. Early submission is often advisable.
Follow Up: Monitor the application process. Some programs may request additional information or conduct interviews as part of the selection process.
Wait for Admission Decision: After submitting your application, patiently await the admission decision. This process may take some time, so be prepared for a waiting period.
Consider Multiple Offers: If you receive multiple offers, carefully consider each program's offerings, faculty, and resources before making a decision.
Accept Admission Offer: Once you've made your decision, formally accept the admission offer from the chosen program.
Remember, each program may have unique requirements, so it's crucial to carefully review the details provided by each institution. Good luck with your application!
What is the eligibility for PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE?
Eligibility criteria for a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference can vary slightly between universities, but here are general requirements commonly observed across programs:
Educational Background:
A Master's degree in Biostatistics, Statistics, Mathematics, or a closely related field is often a prerequisite. Some programs may consider applicants with a strong academic background in these disciplines even if they hold a Bachelor's degree.
Academic Excellence:
Demonstrated academic excellence is crucial. Applicants are typically expected to have a high GPA in their previous academic studies, especially in relevant courses such as statistics, mathematics, or other quantitative disciplines.
Letters of Recommendation:
Most Ph.D. programs in Biostatistics require letters of recommendation. These letters should ideally be from professors, researchers, or professionals who can attest to the applicant's academic capabilities, research potential, and suitability for a doctoral program.
Statement of Purpose (SOP):
A well-written Statement of Purpose is often required. This document should outline the applicant's research interests, academic and professional background, and reasons for pursuing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics.
Standardized Test Scores:
Some programs may require standardized test scores, such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE). Check the specific requirements of each program to determine whether these scores are necessary for your application.
Research Experience:
Research experience, especially in biostatistics or a related field, can enhance an applicant's profile. Highlight any research projects, publications, or contributions to the field in your application.
Relevant Coursework:
Having completed coursework in statistics, mathematics, and related quantitative disciplines is essential. Some programs may specify particular prerequisites or preferred courses.
Professional Experience (Optional):
While not always mandatory, relevant professional experience in areas like biostatistics, data analysis, or research can strengthen an application. Include any applicable work experience in your application materials.
Interview (Possibly):
In some cases, applicants may be required to participate in an interview as part of the selection process. This interview may be conducted in person or virtually.
English Language Proficiency:
International applicants, or those whose primary language is not English, may need to provide proof of English language proficiency through standardized tests like the TOEFL or IELTS.
It's important to note that these are general guidelines, and specific eligibility criteria can vary between institutions. Therefore, prospective applicants should carefully review the admission requirements of the Ph.D. programs they are interested in to ensure they meet all criteria.
How long does it takes to complete a PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE program?
The duration to complete a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference program varies and is influenced by factors such as the structure of the specific program, individual progress, and the nature of the research involved. Typically, a Ph.D. program in biostatistics is designed to be a comprehensive and in-depth academic journey. Here are some general considerations:
Average Duration:
On average, completing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics may take around 4 to 6 years. This duration includes coursework, comprehensive exams, and the completion of the doctoral dissertation.
Coursework Phase:
The initial phase of the program often involves coursework, which can last anywhere from 1 to 2 years. During this time, students take classes to build a strong foundation in biostatistical theory, methods, and related disciplines.
Comprehensive Exams:
Following the coursework, students typically undergo comprehensive exams to demonstrate their mastery of the subject matter. This phase may take several months as students prepare for and complete these examinations.
Research and Dissertation:
The core of the Ph.D. program involves conducting original research and completing a doctoral dissertation. The duration of this phase varies widely depending on the complexity of the research topic, the extent of data collection and analysis, and the writing of the dissertation.
Publication and Defense:
Before completing the program, Ph.D. candidates often aim to publish their research in peer-reviewed journals. The defense of the dissertation before a committee marks the culmination of the program.
Individual Progress:
Individual progress can impact the overall duration. Some students may complete the program in less time, especially if they enter with a strong background in biostatistics or have previous research experience.
Part-Time vs. Full-Time:
The duration may also be influenced by whether a student is enrolled on a full-time or part-time basis. Full-time enrollment typically accelerates program completion, while part-time enrollment allows for a more flexible timeline.
External Factors:
External factors, such as the availability of research resources, funding, and the nature of the research topic, can also impact the time needed to complete the program.
Prospective Ph.D. candidates should review the specific requirements and expectations of the biostatistics programs they are considering, as these can vary among institutions. Additionally, communicating with current students or program coordinators can provide valuable insights into the expected timeline for completion.
What are potential career opportunities after PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE?
Earning a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference opens up a range of rewarding career opportunities. Biostatisticians with advanced degrees are in high demand across various sectors due to their expertise in analyzing and interpreting complex data in the context of healthcare and biological research. Here are some potential career opportunities:
Academic Positions:
Professor/Assistant Professor: Ph.D. graduates can pursue academic positions at universities and research institutions, teaching biostatistics and conducting independent research.
Research Institutions:
Research Scientist: Work as a research scientist in government agencies, private research organizations, or non-profit institutions, contributing to studies that advance medical and biological knowledge.
Healthcare Industry:
Biostatistician in Healthcare: Join healthcare organizations or hospitals as a biostatistician, contributing to clinical trials, epidemiological studies, and data-driven decision-making in healthcare settings.
Pharmaceutical Industry:
Biostatistician in Pharmaceutical Companies: Contribute to drug development and clinical trials by designing studies, analyzing data, and ensuring statistical validity in pharmaceutical and biotech companies.
Government Agencies:
Public Health Analyst: Work for government health agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the National Institutes of Health (NIH), contributing to public health research and policy development.
Consulting Firms:
Statistical Consultant: Offer expertise as a statistical consultant to organizations, helping them interpret and analyze data for decision-making in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and technology.
Epidemiology:
Epidemiologist: Collaborate with epidemiologists to analyze and interpret data related to the spread of diseases, contributing to public health strategies and interventions.
Data Science and Technology:
Data Scientist/Analyst: Apply statistical methods and machine learning techniques in industries outside of healthcare, such as finance, technology, and e-commerce, to extract valuable insights from data.
Government Policy and Regulation:
Regulatory Affairs Specialist: Work with regulatory agencies or pharmaceutical companies to ensure that research and clinical trials comply with regulatory requirements and standards.
Non-Profit Organizations:
Health Research Analyst: Contribute to non-profit organizations focused on health research, playing a key role in designing and analyzing studies aimed at addressing public health challenges.
Global Health Organizations:
Global Health Analyst: Collaborate with international health organizations to analyze global health data, contribute to research, and support initiatives aimed at improving health outcomes worldwide.
Teaching and Training:
Workshops and Training: Conduct workshops, training sessions, and professional development programs to share expertise in biostatistics with researchers, healthcare professionals, and students.
The diverse career paths available to Ph.D. graduates in Biostatistics underscore the importance of their specialized skills in various sectors, contributing to advancements in research, public health, and data-driven decision-making.
Syllabus of PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE
The specific syllabus for a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference can vary among universities and institutions. However, I can provide a general semester-wise outline that typically covers the key areas of biostatistics and research methods. Keep in mind that this is a broad overview, and actual courses may vary based on the program's structure and faculty expertise.
Semester 1:
Biostatistics Foundations:
Introduction to Biostatistics
Descriptive Statistics
Probability Distributions
Mathematical Statistics:
Probability Theory
Statistical Inference
Hypothesis Testing
Research Methodology:
Design of Experiments
Research Ethics
Literature Review and Research Proposal
Computational Statistics:
Introduction to Statistical Software (e.g., R, SAS)
Data Manipulation and Visualization
Semester 2:
Linear Models:
Linear Regression
Multiple Regression Analysis
Model Diagnostics
Categorical Data Analysis:
Logistic Regression
Poisson Regression
Analysis of Contingency Tables
Survival Analysis:
Kaplan-Meier Estimator
Cox Proportional Hazards Model
Time-to-Event Data Analysis
Advanced Probability and Inference:
Advanced Probability Distributions
Bayesian Inference
Non-parametric Methods
Semester 3:
Longitudinal Data Analysis:
Repeated Measures Analysis
Mixed-Effects Models
Growth Curve Modeling
Multivariate Statistics:
Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA)
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
Factor Analysis
Advanced Research Methods:
Causal Inference
Meta-Analysis
Advanced Research Design
Semester 4:
Spatial Statistics:
Spatial Data Analysis
Geostatistics
Spatial Regression Models
Time Series Analysis:
ARIMA Models
Seasonal Decomposition
Forecasting Techniques
Advanced Computational Methods:
High-Performance Computing
Machine Learning in Biostatistics
Big Data Analytics
Special Topics in Biostatistics:
Emerging Trends and Topics in Biostatistics
Guest Lectures and Seminars
Research Phase:
Thesis Research:
Formulation of Research Questions
Data Collection and Analysis
Dissertation Writing and Defense
Publication and Presentation:
Manuscript Preparation for Journals
Conference Presentations
Public Defense of Dissertation
Internship opportunities after completing PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE?
Completing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference opens up various internship opportunities, allowing graduates to apply their advanced skills in real-world settings. Here are some potential internship opportunities that Ph.D. graduates in Biostatistics might explore:
Academic Institutions:
Research Fellowships: Collaborate with professors and researchers on ongoing projects, contributing your expertise to studies in biostatistics and related fields.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech Companies:
Clinical Trial Statistician Intern: Work with pharmaceutical or biotech companies to analyze and interpret clinical trial data, ensuring statistical validity and compliance with regulatory standards.
Healthcare Organizations:
Health Data Analyst Intern: Internships in healthcare settings involve analyzing health data, contributing to epidemiological studies, and supporting evidence-based decision-making.
Government Agencies:
Internship with Health Departments: Work with government health agencies (e.g., CDC, NIH) on public health research projects, contributing your statistical expertise to address health challenges.
Non-Profit Organizations:
Research Analyst Intern: Contribute to non-profit organizations focused on health research, participating in projects aimed at improving public health outcomes.
Data Science and Technology Companies:
Data Science Intern: Explore internships in data-driven industries, applying statistical methods to extract insights from large datasets and contribute to business decision-making.
Consulting Firms:
Statistical Consultant Intern: Gain experience as an intern in statistical consulting firms, working on projects that require statistical analysis and interpretation.
Global Health Organizations:
Internship with International Health Agencies: Collaborate with global health organizations to analyze and interpret global health data, contributing to projects aimed at improving health outcomes worldwide.
Epidemiology Centers:
Epidemiologist Intern: Internships in epidemiology centers involve working on projects related to disease surveillance, outbreak investigations, and public health interventions.
Environmental Health Organizations:
Environmental Biostatistician Intern: Work with organizations focused on environmental health, contributing statistical analysis to studies on environmental factors affecting public health.
Pharmacoepidemiology Research:
Pharmacoepidemiology Intern: Collaborate with researchers studying the effects of pharmaceuticals in large populations, analyzing data to assess drug safety and effectiveness.
Health Analytics Companies:
Health Analytics Intern: Internships in companies specializing in health analytics involve working on projects related to healthcare data analysis, population health, and healthcare management.
Public Policy Research Institutes:
Policy Analyst Intern: Contribute to research projects at institutes focused on public policy, analyzing data to inform health-related policy decisions.
Statistical Software Companies:
Internship with Software Developers: Collaborate with companies developing statistical software, contributing your expertise to improve tools used in the field of biostatistics.
Internships provide invaluable hands-on experience, allowing Ph.D. graduates to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world challenges and build a bridge between academia and professional practice. When exploring internship opportunities, consider the specific focus areas that align with your interests and career goals. Networking, attending conferences, and leveraging university career services can help identify and secure relevant internship opportunities.
Scholarship and grants for PH.D IN BIOSTATISTICS THEORY AND METHODS OF INFERENCE.
Pursuing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference can be financially demanding, but there are various scholarships and grants available to support students during their doctoral studies. Here are some potential avenues for financial assistance:
University-Specific Scholarships:
Many universities offer Ph.D. scholarships specifically for students in biostatistics or related fields. These scholarships may cover tuition, provide a stipend, or both.
Government-Funded Fellowships:
Government agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) or the National Science Foundation (NSF), often offer fellowships and grants to support Ph.D. students in biostatistics. These can include research grants and training fellowships.
Professional Associations:
Organizations like the American Statistical Association (ASA) or the International Biometric Society (IBS) may provide scholarships, grants, or fellowships for students pursuing advanced degrees in biostatistics.
Industry Sponsorships:
Pharmaceutical companies, healthcare organizations, and other industries that heavily use biostatisticians may offer sponsorships or scholarships to Ph.D. students in exchange for research collaborations or internships.
Non-Profit Organizations:
Non-profit organizations focusing on health, research, or education may offer scholarships or grants for biostatistics students. Examples include the Gates Foundation, Wellcome Trust, or the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Research Centers and Institutes:
Institutes specializing in biostatistics or related fields may provide funding opportunities for Ph.D. students. These centers often collaborate with universities and offer financial support for research projects.
International Scholarships:
For students pursuing their Ph.D. in a country other than their home country, there might be international scholarships available. Programs like Fulbright or Chevening provide opportunities for international students.
Diversity and Inclusion Scholarships:
Some scholarships are specifically designed to support underrepresented groups in biostatistics. Check with organizations like the American Indian Science and Engineering Society (AISES) or the Society for Advancement of Chicanos/Hispanics and Native Americans in Science (SACNAS).
Online Scholarship Databases:
Utilize online scholarship databases, such as Fastweb, Peterson's, or the Scholarship Portal, to search for biostatistics-specific scholarships. These platforms often provide a comprehensive list of available opportunities.
Private Foundations:
Private foundations, such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation or the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, may offer scholarships or grants supporting research in health and biostatistics.
Departmental Funding:
Check with the biostatistics department of your chosen university. They may have specific funds, fellowships, or scholarships available for Ph.D. students.
Teaching Assistantships:
Some universities offer teaching assistantships as a form of financial support. This involves assisting with undergraduate courses or labs in exchange for a stipend or tuition reduction.
When applying for scholarships and grants, carefully review the eligibility criteria and application requirements. It's often beneficial to apply to multiple sources to increase the chances of securing financial support for your Ph.D. studies. Additionally, work closely with your university's financial aid office and department to explore all available funding options.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a Ph.D. in Biostatistics: Theory and Methods of Inference is a transformative journey into the heart of statistical research. Armed with advanced knowledge, graduates step into diverse career paths, contributing to healthcare, research, and beyond. Whether pursuing academia, industry, or public health, the impact of biostatisticians resonates globally. Embrace the challenges, seize the opportunities, and embark on a rewarding journey shaping the future of statistical inquiry.
FAQ: 1. What is the duration of a Ph.D. in Biostatistics program?
The average duration is 4 to 6 years, including coursework, comprehensive exams, and dissertation research.
2. What are the career prospects after completing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics?
Career options include academia, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, government agencies, and consulting, with roles such as professor, biostatistician, and research scientist.
3. Are there scholarships available for Ph.D. in Biostatistics students?
Yes, various scholarships and grants are available from universities, government agencies, industry, and professional associations.
4. Can I pursue a Ph.D. in Biostatistics internationally?
Yes, many universities worldwide offer Ph.D. programs in Biostatistics, and international students can explore opportunities through scholarships and fellowships.
5. What skills are developed during a Ph.D. in Biostatistics program?
Students develop analytical skills, critical thinking, and expertise in statistical methods, preparing them for roles in research, academia, and industry.
6. How can I apply for admission to a Ph.D. in Biostatistics program?
The application process typically involves submitting academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, a statement of purpose, and possibly standardized test scores. Check specific program requirements for details.
7. What are the potential internship opportunities after completing a Ph.D. in Biostatistics?
Internship opportunities include academic institutions, healthcare organizations, pharmaceutical companies, government agencies, and consulting firms, providing hands-on experience in applying biostatistical skills.
8. Is financial assistance available for Ph.D. in Biostatistics students?
Yes, students can explore scholarships, grants, fellowships, and teaching assistantships from various sources, including universities, government agencies, and private organizations.
9. What are the key areas covered in the syllabus of a Ph.D. in Biostatistics program?
The syllabus typically includes foundational courses in biostatistics, mathematical statistics, research methodology, and advanced topics like linear models, survival analysis, and spatial statistics.
10. How can I stay updated with emerging trends in Biostatistics?
Stay connected with professional associations, attend conferences, and engage in continuous learning through online platforms and workshops to stay abreast of the latest developments in the field.