Posted by Admin on 21-08-2023 in Shiksha hub
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC), Introduction, Admission, Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
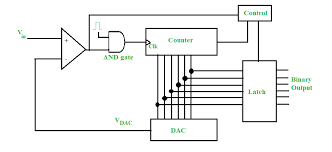
Introduction about ADC
In today's digital age, we encounter countless electronic devices and systems that rely on the conversion of analog signals into digital data. This process is made possible through a fundamental component known as an Analog-to-Digital Converter, or ADC. In this article, we will delve into the world of ADCs, understanding their basic principles, applications, advantages, challenges, and their vital role in modern technology.
Understanding ADC
What is an ADC?
An Analog-to-Digital Converter, or ADC, is an electronic device that plays a pivotal role in converting continuous analog signals into discrete digital values. This conversion allows electronic systems to process and manipulate the data efficiently. ADCs are essential in various applications, from audio and video recording to data acquisition systems.
How does it work?
ADCs operate by sampling the analog signal at discrete intervals and then quantizing these samples into digital values. The analog signal is continuous and can have an infinite number of values, whereas the digital signal consists of finite, discrete values. The process involves two crucial steps: sampling and quantization.
The Basics of ADC
Types of ADC
There are different types of ADCs, including:
Flash ADC: Known for its high-speed performance.
Successive Approximation ADC: Offers a balance between speed and accuracy.
Delta-Sigma ADC: Ideal for high-resolution applications.
Pipeline ADC: Suitable for applications demanding both high speed and high resolution.
Applications of ADC
ADCs find applications in various industries and devices. Some of the key applications include:
In electronic devices: ADCs are found in smartphones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles, where they convert audio and visual data into digital form.
Medical equipment: ADCs are crucial for monitoring and diagnosing patients, as they convert physiological signals into digital data.
Automotive industry: ADCs are used in vehicle control systems for functions like airbag deployment and engine control.
Advantages of ADC
ADCs offer several advantages, including:
Accurate data conversion
Compatibility with digital processing
Improved signal quality
Enhanced data storage and transmission
Challenges and Limitations
While ADCs have numerous benefits, they also face challenges and limitations, such as quantization errors, noise, and power consumption. Engineers continuously work on overcoming these limitations to improve the efficiency of ADCs.
Importance of ADC in Modern Technology
ADCs are the backbone of modern technology. Without them, our digital world would be very different. They enable us to enjoy high-quality audio and video, facilitate the functioning of medical equipment, and even make our vehicles safer and more efficient. The continuous development of ADC technology plays a vital role in shaping our digital future.
Future Trends in ADC
As technology advances, ADCs are expected to evolve as well. Some future trends in ADC technology include higher resolution, lower power consumption, and integration with artificial intelligence, making them even more versatile and efficient.
How can I apply for admission to ADC
To apply for admission to ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter), it's essential to note that ADC typically does not refer to an educational institution or a program that requires admission like a college or university. Instead, ADC stands for Analog-to-Digital Converter, which is a critical electronic component used for signal processing and data conversion.
If you are interested in learning more about ADCs, you can explore various resources, such as online courses, tutorials, and textbooks related to electronics and electrical engineering. These resources can help you understand the principles, working mechanisms, and applications of ADCs.
However, if you are looking for information on how to apply for admission to a specific educational institution or program related to electronics and electrical engineering, you should visit the official website of the institution you are interested in. They will provide details on admission requirements, application procedures, deadlines, and any specific prerequisites for their programs.
What is the eligibility for ADC
The eligibility requirements for ADC, which stands for Analog-to-Digital Converter, can vary depending on the context in which you're referring to it. In the context of electronics and engineering, ADC refers to a component used for signal conversion, and there are typically no eligibility requirements for using or working with ADCs.
However, if you're referring to a specific educational program, certification, or job position related to ADCs, the eligibility requirements would depend on the institution or employer. Here are some common scenarios:
Educational Programs: If you are pursuing a degree in electronics, electrical engineering, or a related field, you might study ADCs as part of your curriculum. To be eligible for such programs, you generally need a high school diploma or equivalent and may need to meet specific admission criteria set by the institution offering the program.
Certifications: Some organizations offer certifications related to electronics and ADCs. Eligibility for certification programs can vary, but they often require a certain level of education or work experience in the field.
Job Positions: If you are seeking a job that involves working with ADCs, eligibility would depend on the specific job requirements set by the employer. Typically, you would need a relevant educational background, such as a degree in electrical engineering, electronics, or a related field. Work experience and knowledge of ADCs may also be required or preferred.
How long does it takes to complete a ADC
The time it takes to complete a program or project related to ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) can vary significantly depending on the specific context. Here are a few different scenarios:
Learning about ADC in an Educational Program: If you are studying ADCs as part of an educational program, such as a course in electronics or electrical engineering, the duration can vary. It might be a semester-long course or a module within a more extended program. A typical course duration can range from a few weeks to a few months.
Certification Programs: Some organizations offer certification programs related to ADCs. The time required to complete a certification can also vary. Some certifications can be completed in a matter of days, while others might take several months, depending on the complexity and depth of the material.
Project Involvement: If you are working on a specific project that involves ADCs, the duration will depend on the scope and complexity of the project. Small projects might be completed in a few weeks, while more extensive projects could take several months or even years.
Job Training: In some cases, learning about ADCs might be part of on-the-job training or orientation. The duration of this training will depend on the employer's specific program and the level of expertise required for the job.
It's important to note that learning about ADCs is not a single, standalone task, but rather a component of a broader educational program, certification, project, or job role. The time it takes to complete ADC-related activities will depend on your specific goals and the context in which you are engaging with ADC technology.
What are potential career opportunities after ADC
Career opportunities after learning about ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) technology can be diverse and depend on your educational background, skills, and interests. Here are some potential career paths and opportunities:
Electronics Engineer: Electronics engineers design, develop, and test electronic systems and components, including those that involve ADC technology. They work in various industries, such as telecommunications, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Electrical Engineer: Electrical engineers specialize in the study and application of electrical systems, which can include the use of ADCs in various applications. They work on power distribution, control systems, and more.
Embedded Systems Engineer: These engineers focus on designing and developing embedded systems that often incorporate ADCs. These systems are used in products like IoT devices, automotive control systems, and medical devices.
Data Analyst: Professionals in data analysis may use ADCs in data acquisition and measurement. They work with large datasets to extract meaningful insights and make data-driven decisions.
Signal Processing Engineer: Signal processing engineers work on the analysis and manipulation of signals, often involving the use of ADCs to convert analog signals into digital data. They are essential in fields like telecommunications and audio processing.
Quality Control Specialist: In manufacturing and production environments, quality control specialists use ADC technology for product testing and quality assurance.
Technical Sales and Support: You can work in technical sales or support roles for companies that produce ADC-related components and systems. Your role would involve helping customers understand and use these technologies effectively.
Research and Development (R&D): Careers in research and development allow you to work on cutting-edge technologies related to ADCs, contributing to innovations in various industries.
Teaching and Education: With expertise in ADC technology, you can become an instructor or educator, sharing your knowledge with students in educational institutions or through online courses.
Consulting: As a consultant, you can provide specialized advice and solutions to organizations looking to implement ADC technology effectively.
Start Your Own Business: If you have innovative ideas related to ADC technology, you can start your own business, developing and selling products or solutions that incorporate ADCs.
Medical Device Engineer: In the healthcare sector, you can work as a medical device engineer, designing and maintaining medical equipment that utilizes ADCs for patient monitoring and diagnostics.
Audio Engineer: If you have a passion for sound and music, you can work as an audio engineer, where ADCs play a crucial role in recording and producing high-quality audio.
Syllabus of ADC
The syllabus for a course on ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) can vary depending on the educational institution, the level of the course, and the specific goals of the program. However, I can provide a general outline of what a semester-wise syllabus for a course on ADC might look like:
Semester 1: Introduction to Electronics and ADC Basics
Week 1-2: Introduction to Electronics
Basic electronic components and circuits
Understanding voltage, current, and resistance
Week 3-4: Introduction to Analog Signals
Analog vs. digital signals
Properties of analog signals
Week 5-6: Introduction to Digital Signals
Basics of binary and digital representation
Digital signal characteristics
Semester 2: Principles of ADC
Week 1-2: Introduction to ADCs
What is an ADC?
Why ADCs are used in electronics
Week 3-4: ADC Architecture and Types
Different types of ADCs
Comparison of ADC architectures
Week 5-6: ADC Resolution and Sampling
Understanding resolution and sampling rate
Factors affecting ADC performance
Semester 3: ADC Circuits and Applications
Week 1-2: ADC Circuits and Components
Operational amplifiers (op-amps) in ADC circuits
Voltage references and clock signals
Week 3-4: Practical ADC Applications
ADCs in sensors and transducers
Data acquisition systems and microcontrollers
Week 5-6: Real-world Case Studies
Analysis of ADC applications in various industries
Semester 4: Advanced Topics and Practical Projects
Week 1-2: Noise and Error Analysis in ADC
Sources of noise in ADCs
Error analysis and mitigation techniques
Week 3-4: Calibration and Testing
ADC calibration methods
Testing and validation of ADC systems
Week 5-6: Final Project
Students work on practical projects involving ADCs
Presentation and evaluation of projects
Internship opportunities after completing ADC
After completing a course or gaining knowledge in ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) technology, you may consider pursuing internship opportunities to gain practical experience in the field. Internships can provide valuable hands-on experience and help you apply your knowledge in real-world situations. Here are some internship opportunities you can explore:
Electronics and Electrical Engineering Intern: Many companies offer internships for students and recent graduates in electronics and electrical engineering. You can work on projects related to analog and digital electronics, including ADC technology.
Embedded Systems Intern: Internships in embedded systems engineering allow you to work on projects involving ADCs, especially if the company focuses on designing embedded systems for various applications.
Data Analysis Intern: If you have a strong understanding of data acquisition and processing using ADCs, consider data analysis internships. You can work with large datasets and gain insights into data manipulation and interpretation.
Manufacturing and Quality Control Intern: Manufacturing companies often offer internships in quality control and product testing. You can gain experience in testing products that include ADC technology.
Research and Development Intern: Companies engaged in R&D projects related to electronics and technology may offer internships. You can contribute to research projects involving ADCs.
Startups and Innovation Hubs: Interning at a technology startup or innovation hub can be an exciting opportunity to work on cutting-edge projects that involve ADCs. Startups often seek interns to assist in product development.
Audio Engineering Intern: If you have a specific interest in audio applications of ADCs, consider interning at recording studios or companies specializing in audio equipment.
Medical Device Intern: In the healthcare sector, you can explore internships with companies that design and manufacture medical devices, where ADCs are integral.
Sensor and Transducer Intern: Companies that produce sensors and transducers may offer internships focusing on the technology used in data acquisition, which involves ADCs.
Telecommunications and Networking Intern: Telecommunications and networking companies often require interns to assist in the development and maintenance of communication systems, many of which use ADC technology.
When searching for internship opportunities, consider industries and companies that align with your interests and career goals. Check with your educational institution's career services, job boards, and company websites to find internship openings. Tailor your resume and cover letter to highlight your knowledge of ADCs and your enthusiasm for the specific field you're interested in. Internships can be a valuable step toward a rewarding career in technology and electronics.
Scholarship and grants for ADC
Scholarships and grants related specifically to ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) technology may be limited, as ADCs are typically a component of broader fields such as electronics, electrical engineering, or data science. However, you can explore scholarships and grants in these related fields that might support your studies and research in ADC technology. Here are some options to consider:
Electrical Engineering Scholarships: Many universities and organizations offer scholarships for students pursuing degrees in electrical engineering. These scholarships can provide financial support for your education and research in areas that may include ADC technology.
Electronic Engineering Scholarships: Scholarships specific to electronic engineering can also be relevant if you are studying ADCs as part of your coursework or research. Check with universities and professional organizations for such opportunities.
STEM Scholarships: Scholarships in the STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) are often broadly applicable to fields that encompass ADC technology. These scholarships can support your academic pursuits.
Data Science Scholarships: If you are focusing on data acquisition and analysis using ADCs, scholarships related to data science and analytics may be beneficial.
Engineering Professional Organizations: Organizations like the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) offer scholarships and grants to their members, which can support research and studies related to ADCs.
University Scholarships: Most universities have their own scholarship programs. Research and inquire about scholarships and grants available within your educational institution, specifically within the engineering or electronics departments.
Research Grants: While not traditional scholarships, research grants from government agencies, foundations, and industry partners can fund your research involving ADC technology. Look for research grant opportunities that align with your interests.
Corporate Sponsorships: Some technology companies and corporations offer sponsorships, scholarships, or internships to students pursuing degrees in fields related to their products and technologies, which may include ADCs.
Minority and Diversity Scholarships: Many scholarships aim to increase diversity in STEM fields. If you belong to an underrepresented group in STEM, you may be eligible for scholarships designed to support diversity in the field.
Professional Development Grants: Some organizations and institutions offer grants for professional development, including continuing education and specialized training. These can be relevant if you want to enhance your skills in ADC technology.
To find suitable scholarships and grants, it's essential to research and apply early, as deadlines and eligibility criteria can vary. Consult your university's financial aid office, visit scholarship search websites, and reach out to relevant professional organizations for the most up-to-date information on available opportunities. Additionally, consider reaching out to professors and mentors who may be aware of specialized funding opportunities in your area of interest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) are unsung heroes of the digital age, facilitating the conversion of analog signals into digital data in a wide range of applications. They offer a bridge between the analog and digital worlds, enabling the technology that surrounds us. With ongoing advancements and innovations, ADCs will continue to play a crucial role in shaping our digital future.
FAQ,s
What is an ADC?
An ADC, or Analog-to-Digital Converter, is an electronic component that converts continuous analog signals into discrete digital values for processing by digital systems.
Why are ADCs important?
ADCs are crucial because they bridge the gap between the analog and digital worlds, enabling the conversion of real-world signals (e.g., audio, temperature, voltage) into data that computers and digital devices can understand and manipulate.
What are the different types of ADCs?
Common types of ADCs include Flash ADCs, Successive Approximation ADCs, Delta-Sigma ADCs, and Pipeline ADCs. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for various applications.
How does an ADC work?
ADCs work by sampling an analog signal at discrete intervals and then quantizing these samples into digital values. The process involves two essential steps: sampling and quantization.
What is ADC resolution, and why does it matter?
ADC resolution refers to the number of bits used to represent the digital output. Higher resolution ADCs can represent more detail in the analog signal, providing more accuracy in the converted data.
In which industries are ADCs commonly used?
ADCs are prevalent in various industries, including telecommunications, consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, industrial automation, and scientific research.
What are the challenges in ADC technology?
Challenges include quantization errors, noise, and power consumption. Engineers continually work on addressing these challenges to improve ADC performance.
How are ADCs used in audio applications?
ADCs are fundamental in audio recording and playback systems. They convert analog audio signals (e.g., music or voice) into digital format, allowing for recording, editing, and playback on digital devices.
What is the role of ADCs in data acquisition systems?
ADCs play a central role in data acquisition systems, where they capture and digitize signals from sensors, instruments, and transducers for further analysis and storage.
What are the future trends in ADC technology?
Future trends include higher resolution ADCs, lower power consumption, integration with artificial intelligence, and advancements in digital signal processing to improve performance and efficiency.