Posted by Admin on 08-07-2023 in Shiksha hub
Blood Bank Technician Admission, Registration, Eligibility, Duration, Fees, Syllabus 2024
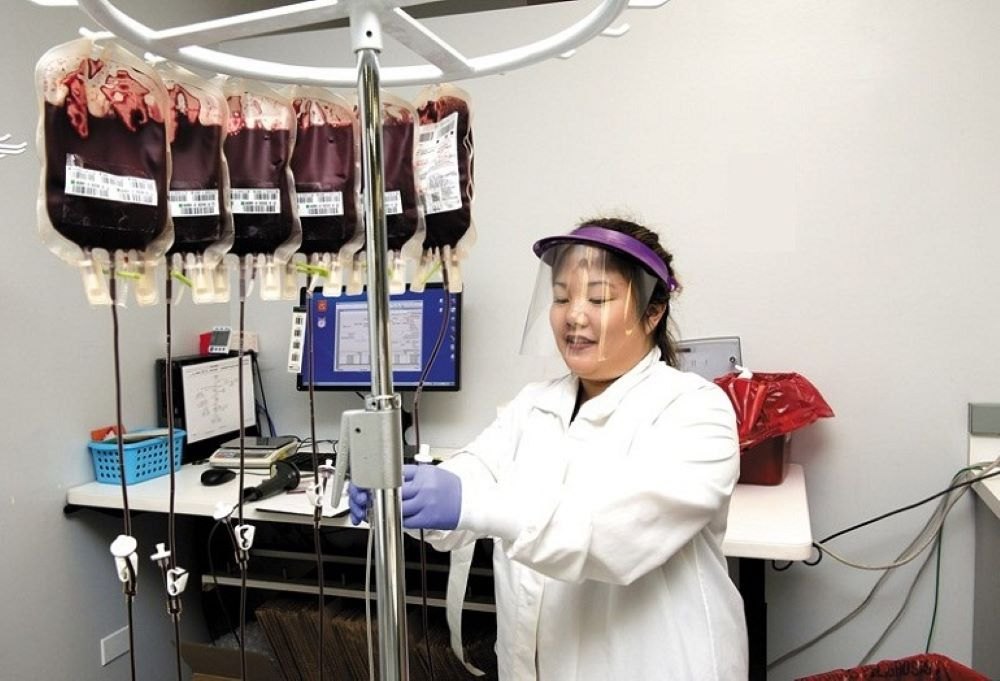
Introduction about Blood Bank Technician
Blood Bank Technicians play a crucial role in the healthcare system, contributing to the availability of safe and sufficient blood supplies for medical treatments and emergencies. Their expertise ensures the proper collection, processing, and testing of blood, making them indispensable in various medical settings.
Importance of Blood Bank Technicians
In the intricate web of healthcare, blood bank technicians are the unsung heroes who ensure that blood donations are collected, processed, and distributed efficiently. Their work is pivotal in saving lives during surgeries, accidents, and medical treatments.
Education and Training
Becoming a blood bank technician requires a combination of academic qualifications and specialized training. A background in medical laboratory technology or a related field is often a prerequisite. Additionally, candidates undergo specific training programs to familiarize themselves with the intricacies of blood banking.
Responsibilities of a Blood Bank Technician
Blood Collection and Processing
One of the primary responsibilities of blood bank technicians is the collection of blood donations. They meticulously process each donation, separating it into its various components such as red blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
Testing and Analyzing Blood Samples
Blood bank technicians conduct rigorous tests to ensure the safety and compatibility of blood products. These tests include screening for infectious diseases and checking blood types to facilitate successful transfusions.
Equipment and Technology Used
The field of blood banking has evolved significantly, with modern equipment and technology playing a crucial role. Automated analyzers, refrigerated storage units, and advanced testing devices contribute to the efficiency and accuracy of blood processing.
Safety Protocols in Blood Banking
Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount in blood banking. Technicians adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent contamination and ensure the integrity of blood products. Stringent regulations govern every step of the process to guarantee the safety of both donors and recipients.
Emerging Trends in Blood Banking
Automation in Blood Testing
The integration of automation in blood testing has streamlined processes, reducing the margin for error and expediting results. Automated analyzers handle large volumes of samples with precision, allowing technicians to focus on more complex tasks.
Integration of Data Technology
Technological advancements extend beyond equipment, with the integration of data technology enhancing record-keeping and traceability. Electronic systems help track blood donations from collection to distribution, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Challenges Faced by Blood Bank Technicians
Despite the advancements in blood banking, technicians face challenges such as a shortage of blood supply and the constant need for accuracy in testing. Meeting the demand for specific blood types during emergencies poses a continuous challenge.
Career Opportunities
Blood bank technicians find employment in diverse settings, including hospitals, blood donation centers, and research institutions. The demand for their skills opens up various career growth prospects, from supervisory roles to specialization in specific areas of blood banking.
Impact of Blood Bank Technicians on Public Health
The contributions of blood bank technicians extend beyond the laboratory. Their work directly impacts public health by supporting medical advancements, contributing to research, and playing a crucial role in emergency situations.
How can I apply for admission to Blood Bank Technician Program
Are you passionate about making a difference in healthcare and contributing to the crucial field of blood banking? Applying for admission to a Blood Bank Technician Program is the first step towards a rewarding career. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to navigate the application process:
1. Research Programs and Requirements
Begin by researching accredited Blood Bank Technician Programs. Look for institutions that offer comprehensive curricula and practical training. Take note of the specific requirements for admission, including educational qualifications and any prerequisite courses.
2. Acquire the Necessary Educational Qualifications
Most Blood Bank Technician Programs require a background in medical laboratory technology or a related field. Ensure that you meet the educational qualifications by obtaining a relevant degree or completing any required coursework.
3. Explore Specialized Training Programs
In addition to academic qualifications, many programs may require or prefer candidates who have undergone specialized training in blood banking. Look for training programs that align with the requirements of your chosen institution.
4. Prepare Application Documents
Assemble all necessary documents for your application. This typically includes transcripts, letters of recommendation, a resume, and a personal statement. Tailor your personal statement to highlight your passion for blood banking and your commitment to the field.
5. Submit a Well-Crafted Personal Statement
Craft a compelling personal statement that showcases your motivation, relevant experiences, and why you aspire to become a Blood Bank Technician. Emphasize any volunteer work, internships, or coursework that demonstrates your dedication to the field.
6. Letters of Recommendation
Secure strong letters of recommendation from individuals who can speak to your academic abilities, work ethic, and suitability for the program. Choose recommenders who can provide insight into your potential success in the Blood Bank Technician Program.
7. Complete the Application Form
Follow the application guidelines provided by the institution and complete the application form accurately. Pay attention to deadlines and ensure all required information is included.
8. Prepare for Interviews
Some programs may require interviews as part of the admission process. Prepare for these interviews by researching common questions related to blood banking and expressing your genuine interest in the profession.
9. Financial Aid and Scholarships
Explore opportunities for financial aid or scholarships offered by the institution or external organizations. Investigate eligibility criteria and deadlines for application.
10. Stay Informed about Admission Decisions
After submitting your application, stay informed about the admission timeline. Check for any updates or requests for additional information. Be patient, as the admission process may take some time.
What is the eligibility for Blood Bank Technician
If you aspire to become a Blood Bank Technician, understanding the eligibility criteria is crucial. This ensures that you meet the necessary qualifications to pursue this rewarding career. Here's a comprehensive guide to the eligibility requirements for aspiring Blood Bank Technicians:
1. Educational Qualifications:
The primary eligibility criterion for becoming a Blood Bank Technician is a relevant educational background. Typically, candidates are required to have:
A high school diploma or equivalent
A degree in medical laboratory technology, clinical laboratory science, or a related field
Having a strong foundation in the sciences, especially biology and chemistry, is beneficial. Some programs may also accept candidates with degrees in health sciences or a closely related discipline.
2. Specialized Training:
In addition to academic qualifications, many institutions and employers prefer candidates who have undergone specialized training in blood banking. This training may include:
Courses focused on phlebotomy and blood collection techniques
Training in the processing and testing of blood samples
Hands-on experience in a laboratory setting, specifically in a blood bank
This specialized training ensures that candidates are equipped with the practical skills necessary for the role of a Blood Bank Technician.
3. Certification:
While certification is not always mandatory, obtaining certification can significantly enhance your eligibility and competitiveness in the job market. Certifying organizations such as the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) offer certifications specific to blood banking, validating your proficiency in the field.
4. Attention to Detail:
Due to the critical nature of their work, Blood Bank Technicians must possess a keen attention to detail. This includes:
Accurate record-keeping of donor information and blood test results
Precise execution of blood collection, processing, and testing procedures
Attention to detail is vital to maintaining the integrity of the blood supply and ensuring the safety of both donors and recipients.
5. Communication and Interpersonal Skills:
Blood Bank Technicians often work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, donors, and laboratory staff. Effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for:
Explaining procedures to donors
Collaborating with colleagues in the laboratory
Conveying critical information regarding blood products
6. Adherence to Safety Protocols:
Maintaining a safe and sterile environment is paramount in blood banking. Eligible candidates must:
Follow strict safety protocols to prevent contamination
Adhere to established hygiene standards during blood collection and processing
7. Physical Stamina:
The role of a Blood Bank Technician may involve long hours on their feet, especially during blood drives or emergencies. Physical stamina is crucial to:
Handle the demands of blood collection and processing
Respond effectively to urgent situations
How long does it takes to complete a Blood Bank Technician program
Duration of Blood Bank Technician Programs: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on a career as a Blood Bank Technician involves undergoing specialized training to acquire the necessary skills for this vital healthcare role. Understanding the duration of Blood Bank Technician programs is crucial for individuals considering this path. Here's a comprehensive guide to the typical duration of such programs:
1. Academic Background:
The duration of a Blood Bank Technician program is influenced by the candidate's academic background. While specific program lengths may vary, candidates generally enter these programs with a foundational education in medical laboratory technology, clinical laboratory science, or a related field.
2. Associate's Degree Programs:
Many aspiring Blood Bank Technicians pursue an associate's degree, which is a common entry-level qualification. Associate's degree programs typically take approximately:
Two Years: This duration includes classroom instruction and hands-on training in a laboratory setting. Candidates delve into courses specific to blood banking, phlebotomy, and laboratory techniques.
3. Bachelor's Degree Programs:
Some institutions offer bachelor's degree programs for individuals seeking a more comprehensive education in laboratory science. These programs generally take:
Four Years: Bachelor's degree programs provide a broader understanding of laboratory science, with a focus on blood banking. The additional two years allow for a deeper exploration of related subjects and may include internships or research opportunities.
4. Certificate or Diploma Programs:
In addition to degree programs, there are shorter certificate or diploma programs tailored specifically for individuals who may already have a degree in a related field or wish to gain targeted training in blood banking. These programs typically take:
Six Months to One Year: Certificate or diploma programs offer a more accelerated pathway for individuals who want to quickly enter the workforce as Blood Bank Technicians.
5. Internship or Clinical Training Period:
Regardless of the level of education pursued, many Blood Bank Technician programs include an internship or clinical training period. This hands-on experience is crucial for applying theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios and may extend the overall duration of the program.
6. Certification Period:
Upon completing the educational component of the program, candidates often pursue certification from recognized organizations such as the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). While certification is not always mandatory, obtaining it can enhance employment prospects. The time required for certification preparation and examination varies.
What are potential career opportunities after Blood Bank Technician
Becoming a Blood Bank Technician opens up a multitude of career opportunities within the dynamic field of healthcare. These professionals play a crucial role in ensuring the availability of safe and sufficient blood supplies. Here's a comprehensive guide to potential career opportunities after completing a Blood Bank Technician program:
1. Hospital Blood Bank Technician:
The most common career path for Blood Bank Technicians is working in hospital settings. They are integral to the healthcare team, responsible for collecting, processing, and testing blood donations. Hospital blood bank technicians collaborate with other medical professionals to support surgeries, emergency treatments, and various medical procedures.
2. Blood Donation Centers:
Blood donation centers are vital in maintaining a steady supply of blood for various medical needs. Blood Bank Technicians in these centers are involved in donor recruitment, blood collection, and ensuring the safe processing of donated blood. This role allows for direct interaction with donors and emphasizes community engagement.
3. Diagnostic Laboratories:
Blood Bank Technicians may find opportunities in diagnostic laboratories, where they contribute to broader laboratory testing beyond blood banking. These settings involve a diverse range of medical tests, and technicians play a crucial role in maintaining quality standards and accuracy.
4. Research Institutions:
For those interested in the scientific aspect of blood banking, research institutions provide exciting career prospects. Blood Bank Technicians can engage in research projects focused on improving blood processing techniques, developing new testing methods, and advancing overall blood banking technology.
5. Public Health Organizations:
Blood Bank Technicians can contribute to public health initiatives by working with organizations focused on blood safety and infectious disease prevention. They may be involved in implementing and enforcing safety protocols, ensuring the quality of blood products, and responding to public health emergencies.
6. Teaching and Training:
Experienced Blood Bank Technicians may transition into teaching roles. They can become educators in educational institutions, training the next generation of blood banking professionals. This career path allows for the sharing of practical knowledge and fostering the growth of aspiring technicians.
7. Quality Assurance and Compliance:
Ensuring adherence to quality standards and regulatory compliance is crucial in blood banking. Blood Bank Technicians may find opportunities in quality assurance roles, where they play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and safety of blood products.
8. Supervisory and Managerial Positions:
As Blood Bank Technicians gain experience, they may advance into supervisory or managerial roles. These positions involve overseeing laboratory operations, managing teams of technicians, and contributing to the strategic direction of the blood banking department.
9. Mobile Blood Units:
Some Blood Bank Technicians may work on mobile blood donation units, traveling to different locations to conduct blood drives. This role combines the responsibilities of a technician with the unique aspect of community outreach.
10. Consulting and Advisory Roles:
Experienced Blood Bank Technicians may choose to become consultants or advisors for healthcare organizations, providing expertise on blood banking processes, safety protocols, and quality assurance.
Syllabus of Blood Bank Technician
If you're considering a career as a Blood Bank Technician, understanding the syllabus of the training program is essential. Blood Bank Technician programs provide a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills necessary for this crucial role in healthcare. Here's a comprehensive syllabus that covers the key areas typically included in these programs:
Module 1: Introduction to Blood Banking
Overview of Blood Banking: Historical perspective and the evolution of blood banking.
Importance of Blood Donation: Understanding the significance of blood donation in healthcare.
Ethics and Regulations: Introduction to ethical considerations and regulatory standards in blood banking.
Module 2: Anatomy and Physiology of Blood
Blood Components: Detailed study of red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
Blood Typing and Crossmatching: Understanding ABO and Rh blood groups, and the principles of crossmatching.
Module 3: Phlebotomy Techniques
Venipuncture: Hands-on training in blood collection techniques.
Donor Recruitment and Screening: Strategies for recruiting donors and screening for eligibility.
Module 4: Blood Collection and Processing
Blood Collection Procedures: Safe and efficient methods for collecting blood donations.
Blood Component Separation: Techniques for processing whole blood into its components.
Module 5: Laboratory Testing in Blood Banking
Compatibility Testing: Principles and procedures for ensuring compatibility between donor and recipient blood.
Infectious Disease Screening: Techniques for screening blood donations for infectious diseases.
Module 6: Quality Control and Assurance
Quality Assurance Protocols: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of blood testing.
Compliance with Standards: Adherence to regulatory standards and safety protocols.
Module 7: Safety Protocols in Blood Banking
Sterilization Techniques: Maintaining a sterile environment in the laboratory.
Handling Biohazardous Materials: Proper procedures for handling and disposing of biohazardous materials.
Module 8: Technological Advancements in Blood Banking
Automation in Blood Testing: Introduction to automated analyzers and their role in blood testing.
Data Technology Integration: Utilizing technology for efficient record-keeping and traceability.
Module 9: Emergency Response and Crisis Management
Emergency Blood Transfusions: Protocols for providing blood in emergency situations.
Crisis Management: Strategies for handling shortages and unexpected challenges.
Module 10: Community Engagement and Education
Blood Donation Drives: Organizing and participating in community blood donation events.
Educating the Public: Strategies for raising awareness about the importance of blood donation.
Module 11: Career Development and Professionalism
Career Opportunities: Exploring diverse career paths in blood banking.
Professionalism and Ethics: Cultivating a professional demeanor and adhering to ethical standards.
Module 12: Practical Training and Internship
Hands-on Experience: Applying theoretical knowledge in a practical setting.
Internship Period: Gaining real-world experience in blood collection, processing, and testing.
Module 13: Certification Preparation
Review of Key Concepts: A comprehensive review of essential concepts covered in the program.
Practice Examinations: Simulating certification exams to prepare candidates for successful completion.
Internship opportunities after completing Blood Bank Technician
Completing a Blood Bank Technician program is a significant achievement, but the journey doesn't end there. Internship opportunities play a crucial role in translating theoretical knowledge into practical skills and preparing individuals for the real-world demands of the profession. Here's a guide to exploring internship opportunities after completing a Blood Bank Technician program:
1. Hospital Blood Banks:
Description: Many hospitals have dedicated blood banks where Blood Bank Technicians play a pivotal role. Interning in a hospital blood bank provides hands-on experience in blood collection, processing, and testing.
Benefits:
Exposure to a variety of blood banking procedures.
Interaction with healthcare professionals and exposure to the hospital environment.
Opportunity to contribute to emergency response situations.
2. Blood Donation Centers:
Description: Blood donation centers are essential hubs for blood collection. Interning in a blood donation center offers experience in donor recruitment, screening, and managing blood drives.
Benefits:
Direct interaction with donors and community engagement.
Experience in organizing and conducting blood donation events.
Insight into the logistical aspects of blood collection.
3. Diagnostic Laboratories:
Description: Some Blood Bank Technicians work in diagnostic laboratories where a range of medical tests is conducted. Interning in such a setting provides exposure to a broader spectrum of laboratory procedures.
Benefits:
Learning additional laboratory testing techniques.
Exposure to different types of samples and testing methodologies.
Understanding the interplay of blood banking with broader laboratory functions.
4. Research Institutions:
Description: For those interested in the scientific aspects of blood banking, internships in research institutions offer opportunities to contribute to ongoing projects and explore advancements in the field.
Benefits:
Involvement in cutting-edge research related to blood processing and testing.
Exposure to the development of new technologies in blood banking.
Contribution to scientific publications and advancements.
5. Public Health Organizations:
Description: Interning with public health organizations involved in blood safety and infectious disease prevention provides insights into the regulatory and public health aspects of blood banking.
Benefits:
Understanding regulatory compliance and safety protocols.
Involvement in public health initiatives related to blood safety.
Exposure to crisis management and emergency response planning.
6. Teaching Hospitals and Educational Institutions:
Description: Some Blood Bank Technician programs are affiliated with teaching hospitals or educational institutions. Interning in such settings allows individuals to observe and participate in educational activities.
Benefits:
Exposure to teaching methodologies in the context of blood banking.
Interaction with educators and experienced professionals.
Opportunities to assist in training programs and workshops.
7. Industry Internships:
Description: Blood bank-related industries, such as companies providing blood bank equipment and technology, may offer internships. These experiences provide insight into the business aspects of blood banking.
Benefits:
Exposure to the latest technologies and equipment in blood banking.
Understanding the industry's role in supporting blood banks.
Opportunities to explore careers in the private sector.
Scholarship and grants for Blood Bank Technician
Embarking on a career as a Blood Bank Technician is an exciting journey, and for many, securing financial support through scholarships and grants can make this path more accessible. Here's a comprehensive guide to available scholarships and grants for individuals pursuing education and training in blood banking:
1. American Association of Blood Banks (AABB) Scholarships:
Description: AABB offers scholarships to students pursuing careers in blood banking, transfusion medicine, and cellular therapies. These scholarships are designed to support education and training in these specialized fields.
Eligibility:
Applicants must be enrolled in an accredited program related to blood banking.
Demonstration of academic excellence and a commitment to the field.
2. American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) Scholarships:
Description: ASCP provides scholarships to students pursuing degrees and certifications in laboratory medicine, including blood banking. These scholarships aim to support individuals dedicated to advancing the field of pathology.
Eligibility:
Students enrolled in a relevant program, such as medical laboratory technology.
Strong academic performance and a passion for laboratory sciences.
3. Clinical Laboratory Management Association (CLMA) Scholarships:
Description: CLMA offers scholarships to students pursuing careers in clinical laboratory management, which may include blood banking. These scholarships support individuals aspiring to take on leadership roles in the laboratory setting.
Eligibility:
Enrolled in a program related to clinical laboratory sciences.
Demonstrated leadership potential and commitment to laboratory management.
4. Red Cross Scholarship Programs:
Description: The American Red Cross may offer scholarship programs to individuals pursuing education in fields related to blood banking and healthcare. These scholarships aim to support future professionals in the blood donation and transfusion field.
Eligibility:
Enrolled in a program relevant to blood banking or healthcare.
Commitment to community service and involvement with the Red Cross.
5. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP):
Description: The HPSP is a scholarship program offered by the U.S. Department of Defense. It supports students pursuing healthcare professions, including medical laboratory technology and related fields involved in blood banking.
Eligibility:
U.S. citizens enrolled in an accredited program.
Commitment to serving in the military after completing education.
6. Local Community Foundations and Organizations:
Description: Many local community foundations and organizations offer scholarships to students pursuing education in healthcare and allied health professions. Check with regional foundations for opportunities specific to your area.
Eligibility:
Varies based on the criteria set by local foundations.
Often involves a connection to the local community.
7. Federal Student Aid (FAFSA):
Description: While not a scholarship, completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) can open doors to federal grants and financial aid. This includes the Pell Grant, which provides financial assistance to eligible students.
Eligibility:
Based on financial need and other criteria.
Available to U.S. citizens or eligible non-citizens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood bank technicians are indispensable in maintaining a safe and sufficient blood supply for medical treatments. Their dedication to ensuring the quality of blood products and their impact on public health underscore the critical nature of their role in the healthcare system.
FAQ's
1. What is a Blood Bank Technician?
A Blood Bank Technician is a healthcare professional responsible for collecting, processing, and testing blood donations. They play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and sufficient blood supply for medical treatments.
2. What education is required to become a Blood Bank Technician?
Typically, a high school diploma or equivalent is required. Many Blood Bank Technicians also complete formal education programs in medical laboratory technology or a related field.
3. Is certification necessary to work as a Blood Bank Technician?
While not always mandatory, obtaining certification from organizations like the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) can enhance job prospects and demonstrate competence in blood banking.
4. Can international candidates pursue a career as a Blood Bank Technician in the U.S.?
Yes, international candidates may be eligible, but they must meet educational and certification requirements. It's advisable to check with individual programs and employers for specific eligibility criteria for international candidates.
5. What career opportunities are available after becoming a Blood Bank Technician?
Blood Bank Technicians can work in hospital blood banks, blood donation centers, diagnostic laboratories, research institutions, and more. They may also explore roles in teaching, management, and consultancy within the healthcare sector.
6. How long does it take to complete a Blood Bank Technician program?
The duration varies. Associate's degree programs typically take two years, while certificate or diploma programs may range from six months to a year. Bachelor's degree programs, if pursued, may take four years.
7. What skills are essential for a career as a Blood Bank Technician?
Key skills include a strong educational background, attention to detail, effective communication, adherence to safety protocols, and physical stamina. Interpersonal skills are crucial for working with donors and healthcare professionals.
8. Are there internship opportunities for Blood Bank Technician programs?
Yes, many programs include internships or clinical training periods, providing hands-on experience in blood collection, processing, and testing.
9. What scholarships and grants are available for Blood Bank Technician education?
Various organizations, including AABB, ASCP, and the American Red Cross, offer scholarships. Additionally, local community foundations, military programs like HPSP, and federal financial aid through FAFSA can provide support.
10. Can Blood Bank Technicians advance to managerial positions?
Yes, with experience, Blood Bank Technicians can advance to supervisory or managerial roles, overseeing laboratory operations and managing teams of technicians.